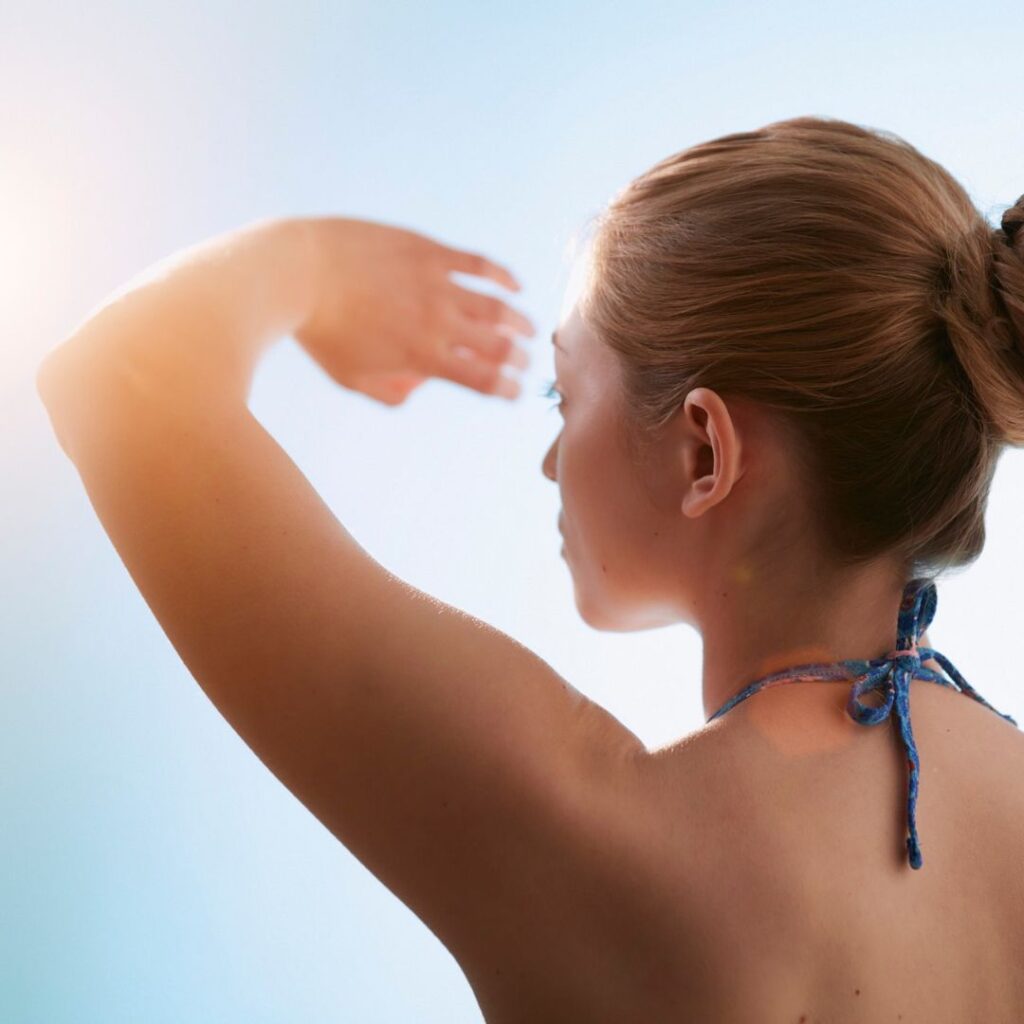
Tanned Skin: Causes, Prevention And Treatment
Table of Contents
ToggleHighlights
- Skin tanning is a natural procedure where the skin darkens in color as it stays exposed to ultraviolet rays.
- Your skin tone may get darker because of the increased melanin production, oxidation of melanin, and increase in the number of melanocytes.
- Skin tanning occurs the most on the temples, forehead, and outer parts of your arms.
- Sunscreen can always help you to protect your skin against harmful UV sun rays.
- All individuals are prone to skin tanning, which depends on factors, such as age, ethnicity, clothing pattern, external activities, and skin type.
- You can develop tanning if your skin gets exposed to UV rays if you are below 5 years and over 50 years.
What Is Tanned Skin?
Body parts (face, hands, legs, feet, and neck) that tend to stay exposed to the sun look darker than those that aren’t exposed to sunlight. As your skin cells get exposed to harmful UV sun rays, they get into protection mode. The melanin from melanocytes gets transferred to keratinocytes, the skin cell surface.
The melanin pigment acts as a protective barrier and blocks UV rays from severe cell damage. The melanin accumulates on the top of the cell nucleus like an umbrella, which occurs in all your skin cells exposed to the sun exposure. Thus, tanning gets visible on all your exposed body parts. It is the process by which your skin pigment (melanin) boosts in your skin after it stays exposed to the sun.
Lighter skin-toned people can’t create a sufficient amount of melanin pigment and thus, their exposed body parts get burned by harmful sun rays. They contain two types of ultraviolet radiation that can harm your skin – Ultraviolet A (UVA) and Ultraviolet B (UVB). The penetration of UVA and UVB rays triggers cells called Melanocytes to produce more melanin and cause tanning.
Your skin’s outer layer contains melanin that causes darkening. Melanin sets the skin tone as its presence decides the fairness and tanning of your body parts. When your skin gets exposed to sun rays, it produces more melanin and develops tanning. Prolonged sun exposure can cause skin damage, such as sunburns, and decrease skin elasticity which causes premature aging.
Causes Of Tanned Skin
Natural sunlight triggers tanning. Even though UV rays cause sunburn and DNA damage to your skin, your body naturally controls, fixes the damage, and protects your skin by producing and releasing more melanin inside the skin cells. Your skin color usually darkens with more melanin production which increases dullness and makes your skin look dull and uneven.
Harmful UV rays create oxidative stress that oxidizes existing melanin and darkens your skin rapidly. Skin darkening caused due to UVA exposure doesn’t boost melanin production or protection against sunburns. UVB radiation triggers a second process where melanin production increases, which is your body’s response to direct DNA photodamage from UV rays.
Here are the key causes of skin tanning:
 UV-A Exposure
UV-A Exposure
UV-A rays are harmful as they can penetrate deep into your skin layer and damage cells. UV-A exposure happens throughout the year as it can pass via the atmosphere’s ozone layer. The increased melanin production of the melanin pigment released from the melanocytes in keratinocytes darkens your skin and makes your skin look brown.
UV-A rays break the natural collagen in your skin, which causes premature aging. Chronic exposure to UV-A rays damages DNA, which is one of the key causes of skin cancer.
 UV-B Exposure
UV-B Exposure
UV-B light burns the upper skin layers and is harmful to its health. Your skin gets more exposure to UV-B light during the summer and less exposure during the winter months. The earth’s ozone layer can block most of the UV-B rays. But, 5 to 10% of UV-B rays can penetrate.
Exposure to UV-B rays intensity DNA damage, which increases melanin production.
Overexposure of your skin to UV-B rays tends to cause moles, sunburns, tanning, aging, and certain types of cancer. UV-B rays can produce more collagen in your skin. Using tanning lamps and equipment also causes pigmented skin.
Types & Classification:
The proper classification of your skin type gives you an estimate of the level of tanning your skin may develop.
Here are the common types and classifications of tanned skin:
- You may never tan if you have Skin Type 1 and pale white skin.
- Your white to light beige complexion may tan the least if you have Skin Type 2.
- Your beige skin may slowly tan to a light-brown shade if you have Skin Type 3.
- Your light brown skin may tan to a dark brown color if you have Skin Type 4.
- Your moderately brown skin may tan to a deeper brown color if you have Skin Type 5.
- Your black or brown complexion may tan a lot if you have Skin Type 6.
Diagnosis:
At Clinic Next Face, our dermatologist can examine and diagnose your skin tan level. Our doctor may ask you to take a physical examination during a consultation as we try to understand the reasons behind and level of tanning.
Are You at Risk?
People of all ages can get a skin tan anytime. Here are the individuals who have the highest risk of getting tan:
- Children below the age of 5 years
- Mature adults over 50 years tend to have thin skin that is more sensitive to harmful UV rays.
- Individuals with weak immunity and chronic diseases are more prone to the side effects of UV exposure.
Prevention and Management:
Here are the measures you can take to prevent and manage skin tanning:
- Apply a sunscreen cream or lotion that protects your skin against UV-A and UV-B rays over a year. It should have an SPF of at least 30 as it works for most types of skin. Some people may require SPF 50 depending on their type of skin. You should use a dermatologist-prescribed sunscreen on your skin.
- Avoid going outside when the sun’s rays are very harsh, mainly from 10 am to 4 pm.
- Wear a scarf or hat on your head and sunglasses to protect your eyes from harmful sun rays
- Wear clothes made of dark and knitted or tightly woven fabric clothes to prevent skin damage caused due to sun exposure.
Self-care:
You can try various home remedies to treat your tanned skin. The remedies can always help to prevent skin tanning. Even though they offer temporary relief, you should consult our dermatologist to get rid of tanning completely.
Treatment Options
Get in touch with Clinic Next Face if you want to treat your suntanned skin well. Here are the two most effective anti-tan treatment methods:
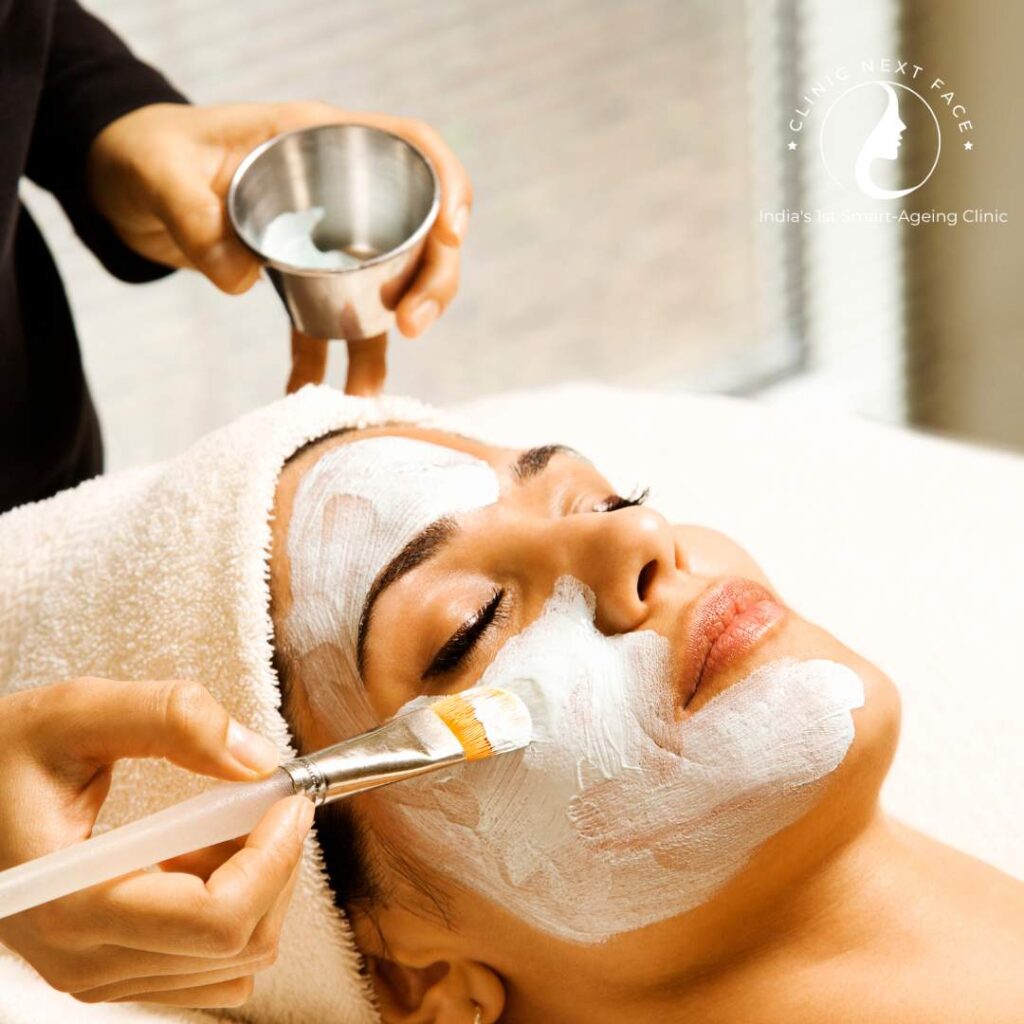
- Chemical Peels
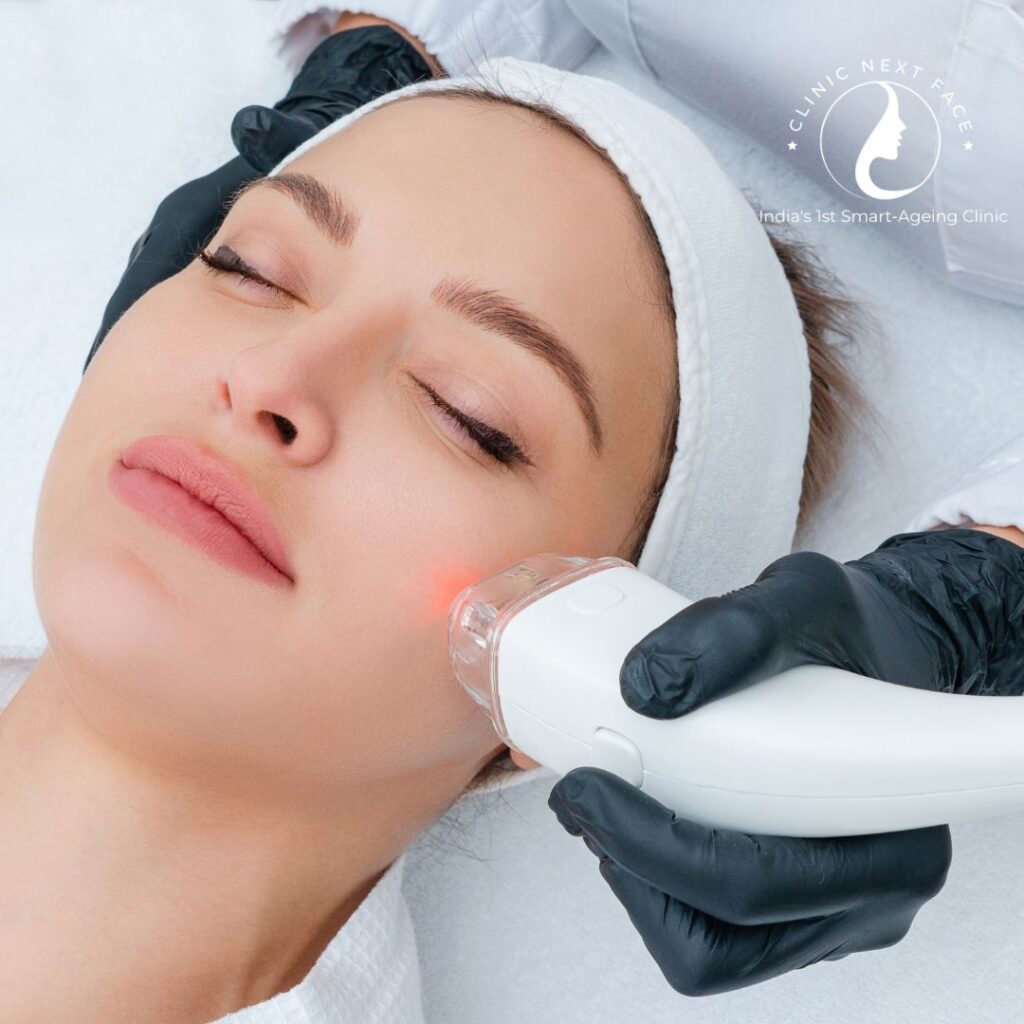
- Laser Toning Treatments

- Topical and Oral Medications
Our skilled and experienced dermatologists at Clinic Next Face can customize a treatment plan suited to your skin tan condition. We can also guide you on post-treatment care for skin tanning to ensure you get the desired and long-term results.
Prognosis
Our dermatologist will work with you in every step to enhance your skin texture after tanning. Book an appointment with our skilled dermatologist to get rid of and protect your skin from tanning.
Clinic Next Face aims to redefine skincare quality and deliver advanced dermatology solutions.
Some of our client’s images from our recent De-tan treatments in Bangalore
Talk To Our Pigmentation Expert Today!
No Obligations! Just jump on a quick call with our pigmentation expert and know what kind of treatment will suit you the best.
Either way you will get some actionable tips to reach your skin goals faster.